Dental restorative materials are used to replace tooth structure loss usually due to dental caries dental cavities but also tooth wear and dental trauma on other occasions such materials may be used for cosmetic purposes to alter the appearance of an individual s teeth.
Ideal properties of dental ceramics.
Their properties vary over a wide range.
The wear between ceramic dental restorations and the adjacent tooth enamel generates another type of defect on the surface of restorations that can be well characterized by sem.
The properties of ceramics are customized for dental applications by precisely controlling the types and amounts of the components used in their production.
Jithendra babu 1 rama krishna alla 2 venkata ramaraju alluri 1 srinivasa raju datla 1 anusha konakanchi 3.
1 for the purposes of this article the term ceramic is used to include all metal free restorations generally all ceramic restorations have been confined to the anterior region until.
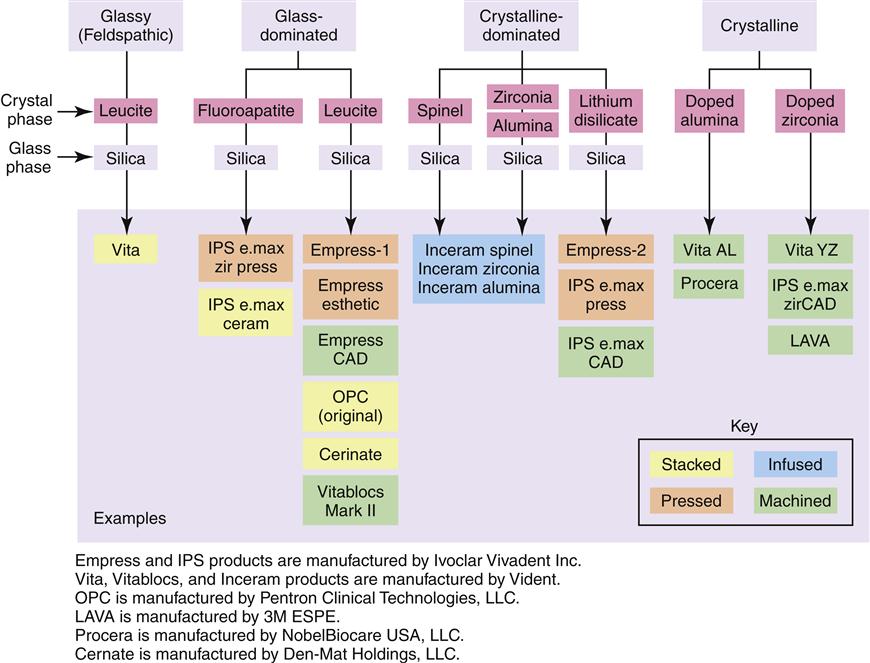
The concern that a ceramic will fracture in service remains a problem for ceramic alloy and all ceramic restorations alike although the newest crystalline ceramics see figure 14 3 are beginning to challenge this notion.
There are many challenges for the physical properties of the ideal dental restorative material.
Part i an overview of composition structure and properties.
For certain dental prostheses such as three unit molars porcelain.
Introduction ceramic is defined as product made from non metallic material by firing at a high temperature.
They also remain stable over long time periods.
Tanja lube robert danzer in advanced ceramics for dentistry 2014.
2 department of dental materials vishnu dental college bhimavaram west godavari andhra.
Two physical properties in particular are used to assess the clinical performance of today s dental ceramics.
Ceramics do not react readily with most liquids gases alkalis and weak acids.
Wear is mainly determined by the friction properties and the micro topography of the restoration porcelain.
Thermal properties are similar to those of enamel and dentine disadvatages high hardness abrasion to antagonist natural dentitions and difficult to adjust.
Dental ceramics can be classified in a number of different ways including by their composition processing method fusing temperature microstructure translucency fracture resistance and abrasiveness.
The term dental ceramics comprises a wide variety of materials that reaches from filled glasses to nearly dense sintered ceramics from products that are shaped from powders and melts to components milled from blanks before or after sintering.